To make the most of your online presence, you need to track the data of your website and understand the performance of how your visitors are interacting with your site. This is where tools like Google Analytics comes in.
Google Analytics is a powerful web analytics tool that allows you to track and analyze various aspects of your website’s performance, such as traffic sources, location, demographics, user behavior, and conversion rates. With this data, you can make informed decisions about how to improve your website and increase engagement with your visitors.
1. How to Set Up Google Analytics?
Creating a Google Analytics account: The first step is to create a Google Analytics account. If you already have a Google account (such as a Gmail account), you can use that to sign in to Google Analytics. If not, you’ll need to create a new Google account.
Setting up a property for your website: Once you’re signed in to Google Analytics, you’ll need to set up a new property for your website. A property is a website or app that you want to track with Google Analytics. To set up a new property, click on the “Admin” tab at the bottom left of the screen, then select “Create Property” from the dropdown menu. As we normally collect the data for website, choose website to start with.
Installing the tracking code on your website: If you’re using WordPress, the Site Kit plugin can simplify the process of installing the Google Analytics tracking code on your website. After installing and activating Site Kit, you can connect it to your Google Analytics account and it will automatically add the tracking code to your website. You can then verify that tracking is working correctly by checking the Analytics tab in the Site Kit menu. With Site Kit, you can easily install and verify the Google Analytics tracking code on your WordPress website without having to manually add code to your site.
2. How to Set Up Goals in Google Analytics?
Setting up goals in Google Analytics is an important step in tracking and measuring the success of your website. Here’s how to set up goals in Google Analytics:
- Log in to your Google Analytics account and select the website you want to set up goals for.
- In the Admin section, click on “Goals” under the View column.
- Click the “+ New Goal” button to create a new goal.
- Choose a goal template or create a custom goal. Google Analytics provides several templates to choose from, such as destination, duration, pages/screens per session, and event goals. You can also create a custom goal based on specific user interactions on your website.
- Set up goal details. Depending on the goal type, you’ll need to enter different details such as the destination URL for a destination goal or the category, action, and label for an event goal.
- Assign a value to the goal. If you want to assign a monetary value to the goal, you can enter a value in the goal details section.
- Verify and save your goal. After setting up your goal, you can verify it by clicking on the “Verify this Goal” button to see if Google Analytics recognizes any conversions. Once you’ve verified the goal, click on “Create Goal” to save it.
2.1 How to Use Google Analytics for Marketing
Here’s an example of how to set up a goal in Google Analytics for “Contact Form Submission”:
2.1.1Creating a Goal Destination Page
- Create a new WordPress page for your thank you page. You can do this by navigating to Pages > Add New in the WordPress dashboard.
- Add content to your thank you page that thanks the user for completing the form and provides any additional information that may be relevant. You can also use this page to promote other content or offers, or to provide links to your social media profiles. Check the “Thank You” Page below and replace with your contents.
In your form settings, specify the URL of your thank you page as the redirect URL after the form is submitted.
2.1.2 Set Up Goals for Your Destination Page
- Log in to your Google Analytics account and select the website you want to set up the goal for.
- In the Admin section, click on “Goals” under the View column.
- Click the “+ New Goal” button to create a new goal.
- Choose “Custom” as the goal type and click “Continue”.
- Enter a descriptive name for the goal, such as “Contact Form Submission”.
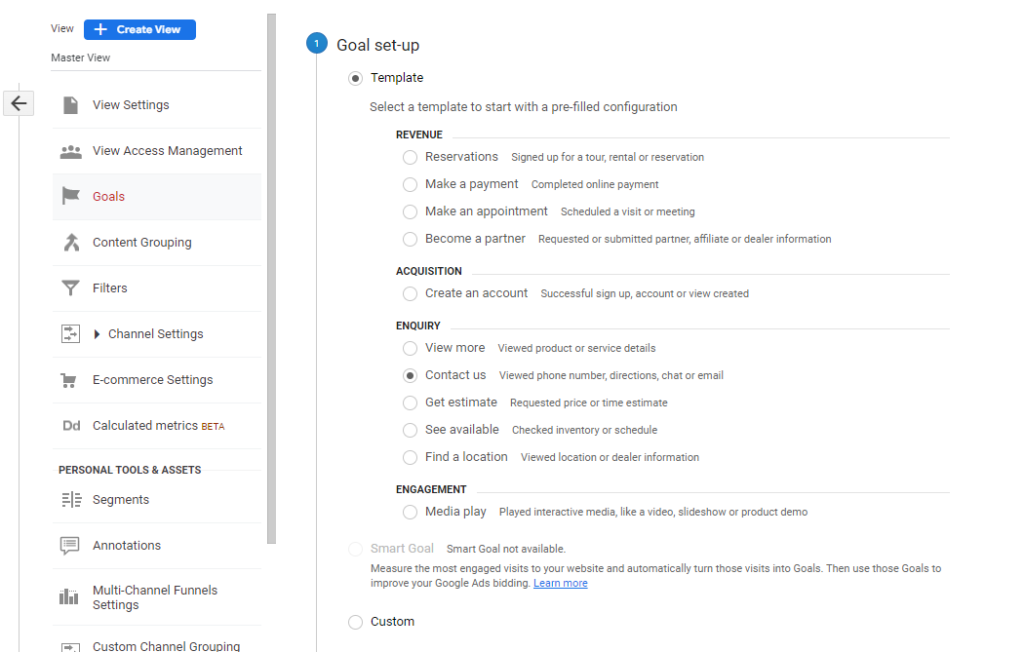
- Select “Destination” as the goal type.

- In the “Destination” field, enter the URL of the thank-you page that appears after the user submits the contact form. For example, if the thank-you page URL is “https://example.com/thank-you“, enter “/thank-you” in the “Destination” field.
- Choose the appropriate match type for the destination URL. This depends on whether the URL is a full URL or just a page path. If it’s a full URL, select “Equals to”. If it’s just a page path, select “Begins with”.
- If you want to assign a value to the goal, you can enter a monetary value in the “Value” field.
- Click “Save” to create the goal.
Once the goal is set up, Google Analytics will start tracking the number of times users complete the contact form and reach the thank-you page. You can then use this data to analyze the conversion rate and other metrics related to the goal in your Google Analytics reports.
3. Important Notice of Google Analytics 4
4. How to Install Google Analytics 4
To install Google Analytics 4 on your website, you’ll need to follow these general steps:
- Create a Google Analytics 4 Property: Sign in to your Google Analytics account and click on the Admin tab. From there, click on “Create Property” and select “Google Analytics 4”. Follow the prompts to set up your new property.
- Add your Property ID to your website: After creating your new property, you will see a Property ID that starts with “G-“. Copy this ID and add it to your website’s tracking code. You can do this manually or by using a tag manager like Google Tag Manager.
- Update your website’s tracking code: If you’re using Universal Analytics on your website, you’ll need to update your tracking code to include the new GA4 tracking code. You can do this by updating your website’s tracking code or by using Google Tag Manager to create a new GA4 tag.
- Test your tracking code: After updating your tracking code, it’s important to test that it’s working correctly. You can use the Google Analytics Debugger extension for Chrome to check that the data is being sent to GA4.
- Verify your tracking code: Finally, verify that your tracking code is working correctly by checking the Real-Time reports in Google Analytics. You should see data starting to appear shortly after you have verified the tracking code.
4.1 Install Google Tag Manager for Your Website
- Log in to your Google Tag Manager account.
- Click on your container name to open the container.
- Click on the “Install Google Tag Manager” button.
- Select the option “Web” and copy the provided code snippet.
- Open the HTML code of your website in a text editor or CMS.
- Find the <head> section of the HTML code.
- Paste the copied Google Tag Manager code snippet into the <head> section of your website HTML code, please check 4.2 for details.
- Save and publish the changes to your website.
4.2 Install HTML Code
- Log in to your WordPress dashboard.
- Navigate to the Appearance section and select the Theme Editor option.
- In the Theme Editor, select the header.php file from the list of theme files on the right-hand side.
- Scroll down through the code to find the <head> section. It will typically be located at the top of the header.php file and will be enclosed in <head> and </head> tags.
- Once you have located the <head> section, you can add the Google Tag Manager code snippet in the section just after the opening <head> tag.
- Log in to your Google Tag Manager account.
- Click on your container name to open the container.
- Click on the “Install Google Tag Manager” button.
- Select the option “Web” and copy the provided code snippet.
- Open the HTML code of your website in a text editor or CMS.
- Find the <body> tag in the HTML code.
- Paste the copied Google Tag Manager code snippet immediately after the <body> tag.
- Save and publish the changes to your website.
4.3 Find the Tag by Source Code
- Open the website you want to add the Google Tag Manager code to in a web browser.
- Right-click on the webpage and select “View page source” or “View source” from the menu. This will open the HTML code of the webpage in a new window or tab.
- In the HTML code, look for the <head> tag and <body> tag. It is usually located near the top of the code, after the <head> tag.
- Once you have located the <body> tag, you can add the Google Tag Manager code snippet immediately after the opening<head> tag and <body> tag.
4.4 Find Tag from Theme File
- Log in to your WordPress dashboard.
- Navigate to the Appearance section and select the Theme Editor option.
- In the Theme Editor, select the head.php file from the list of theme files on the right-hand side.
- Scroll down through the code to find the closing </head> tag. The opening <head> tag will be located near the top of the code.
- Once you have located the closing </head> tag, you can add the Google Tag Manager code snippet immediately before the closing </head> tag.
- In the Theme Editor, select the footer.php file from the list of theme files on the right-hand side.
- Scroll down through the code to find the closing </body> tag. The opening <body> tag will be located near the top of the code.
- Once you have located the closing </body> tag, you can add the Google Tag Manager code snippet immediately before the closing </body> tag.
If you’re not comfortable making these changes yourself, or if you’re not sure how to create a child theme, we recommend contacting the developer team at Easy Marketing for assistance. They can help you integrate Google Analytics 4 with your website and ensure that everything is set up correctly.
Remember, it’s always better to be safe than sorry when it comes to making changes to your website. By taking the time to create a child theme and seeking professional help when needed, you can ensure that your website remains stable and secure.

